Grammy Nominated Comedian, Actor, Writer, Producer, two-time
New York Times best-selling author, three-time Emmy winning top
touring performer, and multi-platinum-selling recording
artist
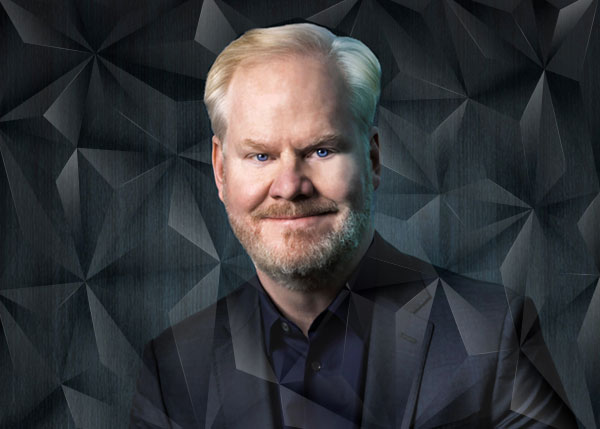
Jim Gaffigan is an eight-time Grammy nominated comedian, actor,
writer, producer, two-time New York Times best-selling author,
three-time Emmy winning top touring performer, and
multi-platinum-selling recording artist. He is known around the
world for his unique brand of humor, which largely revolves around
his observations on life. His 11th special, The Skinny, premiered
on Hulu last winter as the streamer's first ever original stand up
special for their new comedy vertical, Hularious, and garnered
almost 100 million clip views online. Gaffigan is currently on
his, Everything is Wonderful standup comedy tour.
Gaffigan is a top ten comedian according to Forbes' most recent
comedy list and top ten earning comedian in Pollstar. He released
his 10th comedy special, Dark Pale, in 2023 on Amazon Prime Video,
an unprecedented achievement for the comedian/actor. Dark Pale was
met with critical fanfare with The New York Times calling it, 'his
best yet.” Gaffigan recently finished co-headlining with Jerry
Seinfeld for a sold-out multi-city arena tour and in May of 2024,
sold out two shows at The Hollywood Bowl during the Netflix Is
Joke Festival.
In 2021 Gaffigan released his 9th special, Comedy Monster, on
Netflix which was nominated for a Grammy Award. He was also
recently awarded for being the first comedian to reach one billion
streams on Pandora.
Gaffigan can currently be seen opposite co-stars Jerry Seinfeld,
Melissa McCarthy, James Marsden, and Hugh Grant in Netflix's
Unfrosted, which debuted as the #1 movie in the world on Netflix
last May. He can also currently be seen as the lead in the
well-reviewed and certified fresh Sci-Fi drama, Linoleum, which
was named one of Vulture.com's best movies of 2023 and is
currently streaming on Hulu after a theatrical release.
Gaffigan starred as Mr. Smee in Disney's Peter Pan and Wendy,
opposite Jude Law and Yara Shahidi. Also premiering recently,
Gaffigan joined the cast of HBO Max's Full Circle, a limited
series from Steven Soderbergh and Ed Solomon which follows an
investigation into a botched kidnapping, connecting multiple
characters and cultures in present day NY.
On the silver screen, his many credits include Three Kings, Super
Troopers 1 & 2, and Chappaquiddick. 2019 was Gaffigan's biggest
year in film to date with an astonishing eight films releasing,
three which premiered at the Sundance Film Festival including
Troop Zero with Viola Davis and Alison Janney, Them That Follow
and Light From Light - with many festival goers and press calling
Gaffigan the “King of Sundance.” Gaffigan was also recently heard
in Disney/Pixar's highly anticipated animated film, Luca, opposite
Jacob Tremblay and Maya Rudolph.
Gaffigan had two films recently in which he debuted as the lead.
The comedic film Being Frank, and American Dreamer, a dark
thriller which features him as a ride share app worker who
moonlights as a private driver for a drug dealer. Gaffigan can
also currently be seen opposite Ethan Hawke in IFC Films Tesla, as
well as opposite Josh Hartnett in Saban Films' Most Wanted.
In addition to two seasons of the critically acclaimed
semi-autobiographical The Jim Gaffigan Show, which he wrote and
produced with his wife Jeannie, Gaffigan has guest starred on many
television comedies and dramas, ranging from Portlandia and Bob's
Burgers to the HBO cult hits Flight of the Concords to dramatic
roles in Law & Order.
Gaffigan regularly does humorous commentaries on CBS Sunday
Morning for which he has won 3 Emmys. In 2018 Jim served as master
of ceremony at The Al Smith Memorial dinner. In 2015, Gaffigan had
the great honor of performing for Pope Francis and over 1 million
festival attendees at the Festival of Families in Philadelphia.
He and his wife currently live in Manhattan with their five loud
and expensive children.
 SUPPLY CHAINS.
SUPPLY CHAINS.
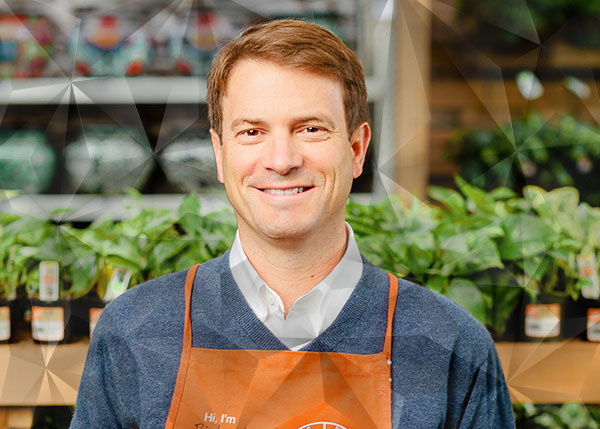 MODEX MONDAY
MODEX MONDAY
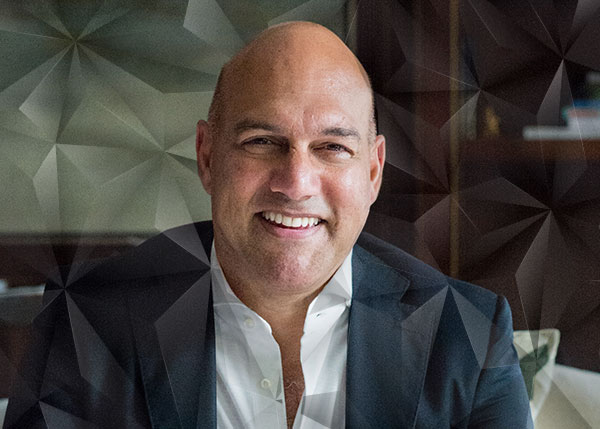 MODEX TUESDAY
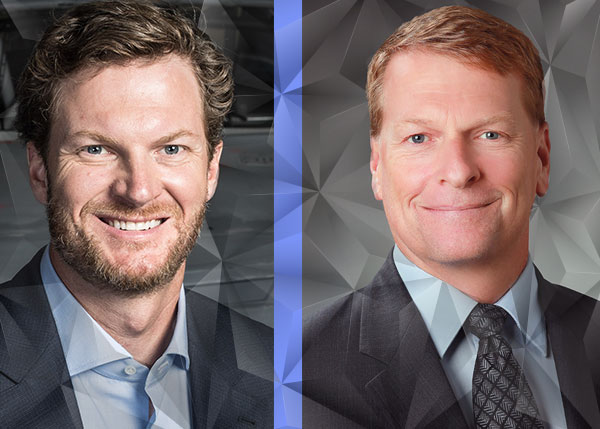
MODEX TUESDAY
 MODEX WEDNESDAY
MODEX WEDNESDAY
 MHI INDUSTRY NIGHT
MHI INDUSTRY NIGHT
 EDUCATION
EDUCATION
 SEARCH
SEARCH
